Introduction
When we talk about essential industrial chemicals, HCOOCH CH2 H2O — commonly known as ethylene glycol — stands out for its versatility and impact across industries. This colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting liquid plays a key role in manufacturing, automotive care, heating and cooling systems, and more. But behind its usefulness lies a chemical that demands respect due to its toxicity and environmental concerns.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what HCOOCH CH2 H2O is, its chemical and physical properties, industrial applications, safety considerations, and future trends in its production and use.
What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is an organic compound scientifically known as 1,2-ethanediol. It’s a diol — meaning it contains two hydroxyl (-OH) groups — which gives it unique chemical reactivity. While often written simply as C₂H₆O₂ in chemical shorthand, the formula representation HCOOCH CH2 H2O emphasizes its structural elements.
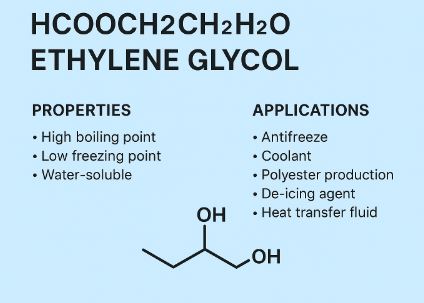
Ethylene glycol’s molecular structure gives it several standout features:
- Complete miscibility with water (thanks to its polar nature)
- High boiling point and relatively low freezing point
- Ability to depress the freezing point of water dramatically when mixed
These characteristics make it indispensable in applications like antifreeze, de-icing solutions, polyester production, and heat transfer fluids.
Chemical and Physical Properties of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1,2-Ethanediol |
| Molecular Formula | C₂H₆O₂ |
| Molar Mass | 62.07 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless, odorless liquid |
| Boiling Point | ~197.3 °C (387.1 °F) |
| Freezing Point | ~ -12.9 °C (8.8 °F) pure, ~ -37 °C (with 50% water mix) |
| Solubility | Fully miscible in water |
| Viscosity | More viscous than water |
| Taste | Sweet (but highly toxic) |
Key characteristics that make HCOOCH CH2 H2O valuable:
- Freezing Point Depression – Perfect for cold-weather engine protection.
- High Boiling Point – Ensures stability in high-temperature systems.
- Hygroscopic Nature – Absorbs moisture from the air, affecting storage.
- Chemical Reactivity – Participates in esterification, etherification, and polymerization.
Production Process of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
The most common method for producing ethylene glycol involves hydration of ethylene oxide:
- Ethylene oxide is produced by oxidizing ethylene gas.
- Ethylene oxide reacts with water in the presence of an acid or base catalyst.
- The reaction yields ethylene glycol in high efficiency with minimal by-products.
This process supports global demand for ethylene glycol in antifreeze, polyester production, and industrial applications.
Top Industrial and Commercial Uses of HCOOCH CH2 H2O
1. Antifreeze and Engine Coolants
The best-known application of HCOOCH CH2 H2O is in antifreeze solutions.
- When mixed with water (usually 50/50), it lowers freezing points and raises boiling points.
- Prevents engine freeze damage in winter and overheating in summer.
- Widely used in cars, trucks, and heavy machinery.
2. Polyester (PET) Production
Ethylene glycol is a key monomer in making polyethylene terephthalate (PET) — the plastic used in:
- Beverage bottles
- Food packaging
- Synthetic fibers for clothing and carpets
- Industrial films
It reacts with terephthalic acid to produce PET, which is durable, lightweight, and recyclable.
3. De-Icing Solutions
Airports and airlines use HCOOCH CH2 H2O in de-icing fluids for aircraft and runways.
- Prevents ice build-up that can disrupt aerodynamics.
- Works quickly to dissolve ice layers.
- Environmental concerns are prompting research into greener alternatives.
4. Heat Transfer Fluids
Beyond car radiators, HCOOCH CH2 H2O is used in:
- HVAC systems
- Industrial chillers
- Solar thermal systems
Its stability under temperature extremes makes it ideal for maintaining efficient heat exchange.
5. Hydrate Inhibition in Pipelines
In the oil and gas industry, ethylene glycol prevents hydrate formation in natural gas pipelines — ice-like blockages that can disrupt flow.
6. Chemical Intermediate
Ethylene glycol is a building block for other chemicals:
- Glycol ethers – solvents for paints, inks, and cleaners
- Plasticizers – make plastics flexible
- Resins – used in adhesives, coatings, and composites
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
While extremely useful, HCOOCH CH2 H2O is highly toxic if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed through skin.
Toxicity Mechanism
- Ethylene glycol itself is less harmful than its metabolites:
- Glycolic acid and oxalic acid damage kidneys and other organs.
- Small amounts can be lethal to humans and pets.
Symptoms of Poisoning
- Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain
- Confusion, dizziness, and slurred speech
- Seizures, kidney failure, and coma
Prevention and Handling
- Store in labeled, sealed containers away from children and pets.
- Clean spills immediately.
- Consider propylene glycol-based antifreeze, which is less toxic.
Environmental Concerns
Even though ethylene glycol is biodegradable, spills can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic ecosystems.
- Impact on water bodies – Consumes oxygen during breakdown, stressing fish populations.
- Airport runoff – De-icing fluid runoff can damage nearby ecosystems.
- Regulatory measures – Increasingly strict controls on discharge and waste handling.
Future Trends in HCOOCH CH2 H2O Use
The future of ethylene glycol is shaped by sustainability goals and regulatory changes:
- Bio-Based Production – Using biomass instead of petroleum feedstocks.
- Greener Coolants – Developing low-toxicity alternatives for antifreeze.
- Advanced Recycling – Improving PET plastic recycling efficiency to reduce demand for virgin ethylene glycol.
Conclusion
HCOOCH CH2 H2O (ethylene glycol) is a cornerstone industrial chemical — from keeping engines running in extreme temperatures to producing the polyester fibers and bottles we use daily.
However, its toxicity and environmental footprint mean it must be handled responsibly. As technology advances, bio-based production, eco-friendly coolants, and improved recycling could transform how we use this valuable but potentially hazardous compound.
By understanding its properties, uses, and safety guidelines, industries and consumers can benefit from ethylene glycol while working toward a more sustainable future.
Also Read: Foenegriek: The Complete Guide to Its Uses, Benefits, and History
Also Read: Shane Deary: The Quiet Woodworker Shaping Brooklyn’s Most Beautiful Homes
[…] The Complete Guide to Dominating Evony Like a Pro HCOOCH CH2 H2O: Properties, Uses, Safety, and Environmental Impact Explained Shane Deary: The Quiet Woodworker Shaping Brooklyn’s Most Beautiful Homes Foenegriek: The […]